What are the Private Cloud Benefits and Challenges? 10 Pros and Cons You should know

A private cloud is a type of cloud computing that, through a private architecture, provides many of the same private cloud benefits and challenges, including scalability and self-service. While public clouds offer services to numerous enterprises, private clouds are focused on the requirements and objectives of a single organization. Therefore today, together with Cloud.tapchiai.net, we will see private cloud benefits and challenges below.
Contents
What Is Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment where all hardware and software resources are dedicated to a single customer and only that customer has access to them. It is sometimes referred to as an internal cloud or corporate cloud. In a private cloud, on-premises infrastructure’s access control, security, and resource customisation are paired with many of the benefits of cloud computing, including elasticity, scalability, and ease of service delivery.
Many businesses prefer the private cloud over the public cloud because it is simpler to comply with regulatory compliance standards than the public cloud. Others want the private cloud because their workloads include sensitive information such as medical records, financial data, intellectual property, and confidential papers.
A private cloud deployment’s higher level of control for the business is one of its most important benefits. Since only one organization has access to the private cloud, it is able to design and administer the environment according to its unique computing requirements.
Hardware that is either locally stored at a company’s location or hosted by a cloud server provider might be used in a private cloud strategy. Although virtual private clouds are typically billed on a monthly basis, the advantages of a safe, private network are maintained with the right hardware and storage settings.
The Types of Private Cloud
Depending on the needs of the business, private clouds can be hosted, maintained, and perform a number of services, including:
Hosted
In a hosted private cloud environment, there is no shared use of the servers with other companies. The server is only used by one business, despite the fact that the service provider sets up the network, maintains the hardware, and updates the software.
Virtual
A walled-off environment within a public cloud called a virtual private cloud enables a business to run its workloads separately from other customers. Even if the server is shared by other companies, the virtual logic ensures that a user’s computer resources are private. The deployment of a hybrid cloud can be facilitated by the usage of a virtual private cloud (VPC).
Managed
In a hosted environment, every aspect of the cloud for the company is maintained by the provider, including the installation of extra services like identity management and storage. For businesses who lack the resources to operate private cloud systems independently, this is an excellent alternative.
The Private Cloud Benefits And Challenges
Private Cloud Benefits
The main advantage of a private cloud over a public cloud when running applications over time and at scale is greater economics. While other features of the cloud are enhanced, a well-designed private cloud has capabilities that are equivalent to those of large public cloud service providers.
1. Security and Conformity
Although private clouds are often regarded to be more secure than public clouds, in some circumstances having total control over the underlying infrastructure might assist enterprises in adhering to compliance standards.
2. Permanent Cost Savings
Even while building a private cloud infrastructure requires a sizable upfront investment, it pays off over time, even with many portable virtual computers.
3. Architectural Independence
When building a private cloud, the business decides what hardware and software to use, improving flexibility and architectural freedom.
4. Customization
A private cloud is created on-site by a cloud architect, enabling stakeholders to specify the precise environment needed to run proprietary applications. Hosted private clouds offer the same advantages as on-premise private clouds, but they don’t need to be set up on-site. In that case, the business works with a partner to create and maintain a cloud that is exclusively for its use.
5. Pricing Predictability
The price of a public cloud is completely unexpected because of many extra costs. Contrarily, private cloud pricing is often completely transparent, enabling predictable budgeting.
6. Integration of Hybrids
When an application needs greater processing power, hybridization expands the resources of a private cloud into a public cloud to ensure uptime without the need to set up additional physical servers. Businesses who need the security of a private cloud but also need the capacity of a public cloud service for other purposes may find this to be a more affordable choice.
7. Increased effectiveness
Since private clouds are operated on-site by an enterprise and do not share resources, they frequently offer better performance than public cloud infrastructure.
Private Cloud Challenges
Although private clouds have many advantages for enterprises, setting up a private cloud infrastructure has its own set of challenges. Here are a few examples:
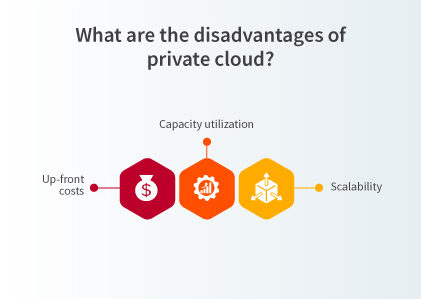
1. Adaptive Scalability
As long as more resources are available in the data center, a private cloud can dynamically scale-out when its resources are depleted. If specific resources are not accessible, it can take some time because of the drawn-out procurement process.
2. Capacity Control
To ensure the desired resource consumption in a private cloud environment, organizations are in charge of capacity management. The internal staff members who manage cloud operations now have more work to do. With the implementation of an appropriate observability stack, continuous private cloud monitoring and proactive capacity control are guaranteed.
3. Costly Capital Investments
Due to their higher initial hardware and software expenses, private clouds are less alluring than public clouds. They’ll eventually recognize the financial benefits. Businesses should always create their private clouds to be economical in order to deal with this. As your needs evolve, start small and expand.
The bottom line
Although there are private cloud benefits and challenges, organizations must proactively guarantee that security is strong and current in order to benefit from private cloud services. As long as a company is vigilant about security, the private cloud can offer a number of benefits in terms of security. Physical security may be simpler to manage because private clouds are only capable of using specific pieces of hardware.
Most private clouds are secured by a perimeter firewall and accessed by personal, secure network lines rather than the public internet. Furthermore, a company’s level of control over its private cloud may make it simpler to comply with governance and regulatory compliance requirements.
Conclusion: So above is the What are the Private Cloud Benefits and Challenges? 10 Pros and Cons You should know article. Hopefully with this article you can help you in life, always follow and read our good articles on the website: Cloud.tapchiai.net